
Electric vehicles (EVs) have become increasingly popular as sustainable and eco-friendly transportation options. As EV technology continues to advance, one of the crucial factors that determine the efficiency and speed of charging is the Direct Current (DC) charging voltage. In this article, we will delve into the details of the DC charging voltage of electric vehicles and its significance.
DC charging voltage refers to the electrical potential that powers the charging process in electric vehicles. Unlike Alternating Current (AC) charging, which is commonly used for home charging, DC charging offers faster and more efficient charging solutions for EVs. The DC charging voltage is typically higher than the voltage used for AC charging.
Electric vehicle charging stations that provide DC charging are equipped with substantial power output capabilities to ensure a swift and convenient charging experience for EV owners. The DC voltage is directly connected to the vehicle's battery, delivering power at high speeds, significantly reducing charging time compared to AC charging.
The DC charging voltage requirements for electric vehicles can vary depending on several factors:
Battery Capacity: The capacity and type of battery installed in the EV can influence the required DC charging voltage. Different EV models come with various battery capacities, which determine the voltage range suitable for charging.
Charging Station Capabilities: The charging station's voltage output capacity is crucial to understand when determining the DC charging voltage. Charging stations may offer various power levels, such as 50 kW, 100 kW, or even higher, each corresponding to a specific voltage range.
Vehicle Specifications: EV manufacturers provide recommended DC charging voltage levels for their specific models. These specifications are designed to ensure optimal charging performance and battery longevity.
While specific DC charging voltage levels vary, the industry has adopted a few common standards:
CHAdeMO: This is a fast-charging standard developed in Japan and widely adopted by various EV manufacturers. CHAdeMO chargers typically operate at 500 volts DC, enabling fast charging times for compatible EVs.
CCS (Combined Charging System): CCS is another widely used standard, especially in the United States and Europe. It supports both AC and DC charging and typically operates in the range of 200-1000 volts DC.
Supercharger Network: Tesla's Supercharger network uses a proprietary charging system that operates at around 400 volts DC. Tesla vehicles can achieve exceptionally fast charging times using this network.
Chinese GB/T: In China, the GB/T DC charging standard operates at voltages up to 1000 volts DC and provides rapid charging capabilities for various EV models.
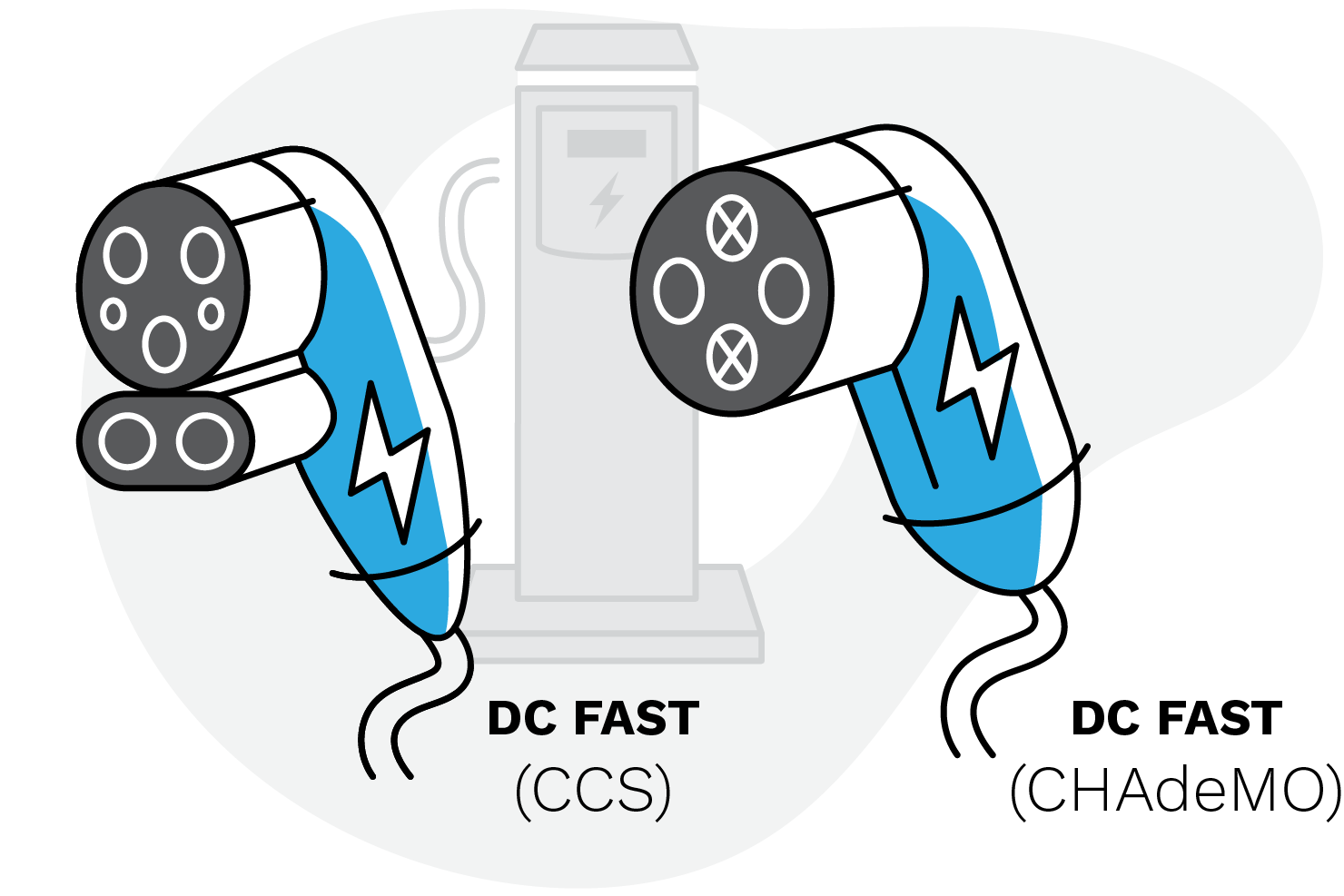
image from calevip.org
The DC charging voltage of electric vehicles plays a crucial role in ensuring efficient and fast charging experiences. Understanding the various factors and industry standards related to DC charging voltage helps to optimize the charging process and embrace the sustainable future of electric transportation.